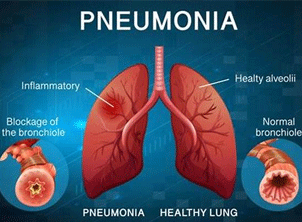
Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes inflammation in the air sacs (alveoli) of one or both lungs, leading to fluid or pus accumulation. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or aspiration of food or liquids. Common symptoms include fever, chills, cough with mucus, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and confusion, especially in older adults. Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-ray, blood tests, and sputum analysis. Treatment depends on the cause—bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics, viral pneumonia with supportive care and sometimes antivirals, while fungal pneumonia requires antifungal medications. Supportive treatments like oxygen therapy, pain relievers, and fluids help manage symptoms. Prevention includes vaccinations (such as pneumococcal and flu vaccines), good hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding smoking. While pneumonia can be serious, early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve recovery chances. If symptoms persist or worsen, immediate medical attention is crucial.